Adafruit N20 DC Motor with Magnetic Encoder - 6V with 1:298 Gear Ratio
Description
The first step in a robotics project is getting a motor spinning. Not all motors spin at the same speed due to variations in voltage, environment, and manufacturing. Determining motor speed involves using an encoder wheel with an optical or magnetic counter to count rotations.
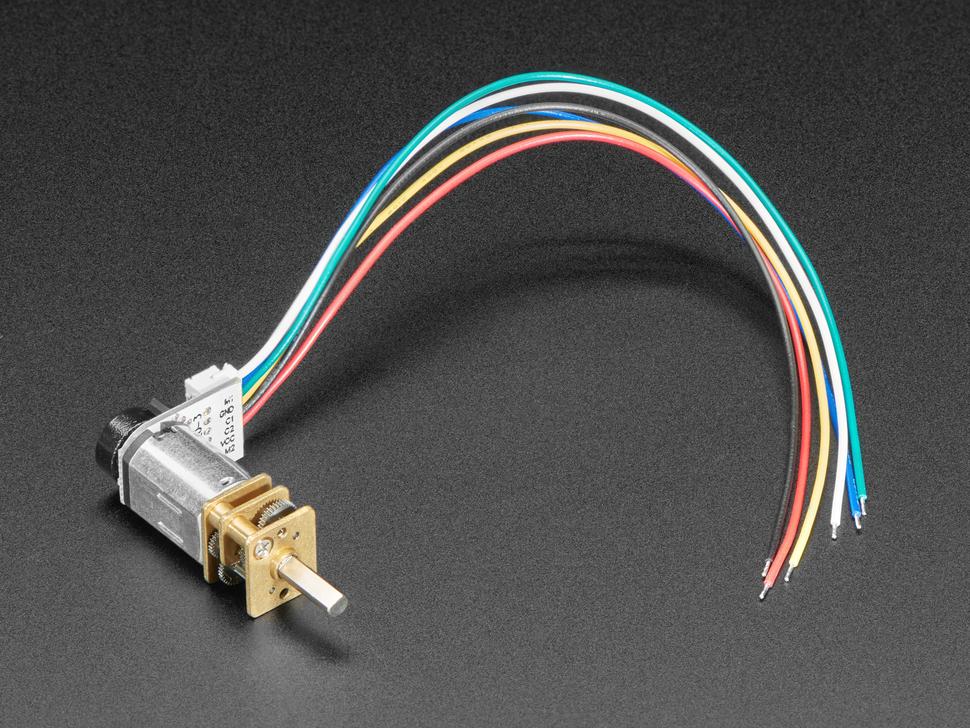
This motor simplifies the process with an attached magnetic wheel and two hall effect sensors, eliminating complex wiring. It's compact, fitting into the standard N20 size, and operates efficiently with 4.5 to 6V DC. Connections are straightforward: white and red wires for motor driving, PWM support for speed adjustment, blue wire for ground, and black wire for power. The yellow and green wires provide encoder outputs.
An example Arduino sketch is available, adaptable to other languages, for interrupt counting and speed calculation using a 1:298 gear ratio. The motor uses 6V nominal power, drawing around 100 mA (200 mA stalled), and varying the gear ratio affects torque and RPM, not current draw.
Properties
| Brand | Adafruit |
| Model | 4641 |
Delivered in 10 to 30 days
Customer questions
Customer Reviews
- In stock Adafruit IR Break Beam Sensor with Premium Wire Header Ends - 5mm LEDs € 7,50 View product
- In stock Adafruit White LED Backlight Module - Medium 23mm x 75mm € 3,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit Pressure-Sensitive Conductive Sheet (Velostat/Linqstat) € 6,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit Speaker - 40mm Diameter - 4 Ohm 5 Watt € 6,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit NOOds - Flexible LED Filament - 3V 300mm long - Warm White € 5,75 View product
- In stock Adafruit Breadboard-friendly SPDT Slide Switch € 1,25 View product
- 5 pieces In stock Adafruit NeoPixel Diffused 5mm Through-Hole LED - 5 Pack € 6,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit NOOds - Flexible LED Filament - 3V 300mm long - Blue € 9,50 View product
- In stock Adafruit Conductive Rubber Cord Stretch Sensor + extras! € 12,75 View product
- In stock Adafruit Bone Conductor Transducer with Wires - 8 Ohm 1 Watt € 11,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit Stacking Headers for Feather - 12-pin and 16-pin female headers € 1,75 View product
- In stock Adafruit USB C Jack to USB C Jack Round Panel Mount Adapter € 9,50 View product
- In stock Adafruit bq25185 USB / DC / Solar Charger with 3.3V Buck Board € 11,25 View product
- In stock Adafruit JST PH 2-Pin Cable – Male Header 200mm € 1,- View product
- In stock Adafruit Stereo Enclosed Speaker Set - 3W 4 Ohm € 9,50 View product










